Varicocele
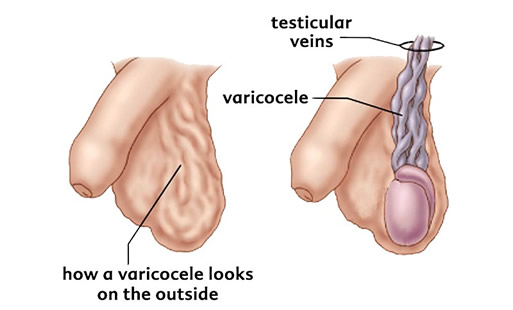
Varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus, the structure responsible for venous drainage of testicles, usually unilateral. It is much more common on the left side because of the anatomy of the blood vessels.
What are the symptoms of varicocele?
- Patients state that they have experienced enlargement in the scrotum, most often on the left side
- Sometimes swelling occurs, which varies throughout the day
- The swelling is located above the testicle and has an irregular "wormlike" appearance
- Pain may also occur, which changes depending on the physical activity
- In many cases, varicocele does not cause any problems
How is a varicocele diagnosed?
- Based on the information we get from the patient
- The usual clinical examination of the genitals verifies the presence of a soft, painless mass in the scrotum
- Ultrasound examination of scrotum - verifies enlargement of testicular veins and can be diagnosed with certainty
- In adults and adolescents, sperm findings are also checked
What are the consequences of untreated varicocele?
Varicoceles can cause problems for the patient and sometimes can lead to damage in the testicle itself. The testicles are located in the scrotum, outside the abdominal cavity and have a lower temperature. In this way their natural function is enabled. Varicocele causes a rise in the local temperature and a delay in the removal of harmful substances from the blood. All this can lead to a decreased size of the testicle, its damage and infertility.
How is varicocele treated?
Treatment is purely surgical.
When is a varicocele operated?
Not all patients with varicocele have an indication for surgery. The operation is performed in case there is:
- Changes in testicular shape and size
- Changes in the quality of the testicular tissue, which are detected by ultrasound examination
- Significant testicular asymmetry
- Testicular growth and development disorder - if it is an adolescent patient
- Problems that disrupt the patient's quality of life
- Inability to conceive (infertility), or poor sperm findings
- Aesthetic and psychological reasons
What does varicocele surgery look like?
Varicocele surgery by open access is the most commonly used technique and is the "gold standard" in the treatment of varicocele.
- It provides better visibility of the region itself, and the surgeon can also use magnification when working if necessary (called microscopic varicocelectomy).
- The varicocele is accessed through a small incision in the groin region.
- The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia.
- The patient stays in the hospital for one day, or leaves for several hours after surgery
- If necessary, painkillers are prescribed
- The patient returns to normal activities after 2 days, with sparing from physical activity for the next two weeks.
- If the reason for performing the procedure was a bad sperm finding, after six months the analysis is repeated and after one year the maximum effect of the surgery is expected.
- Laparoscopic varicocele surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Through a small incision in the abdomen, the urologist accesses the altered veins and interrupts blood flow by inserting a so-called ligation clips.
The decision on whether to perform laparoscopic surgery or classic surgery is made by the doctor in consultation with the patient, depending on the patient's local findings, age and general condition.

