Peyronie's disease

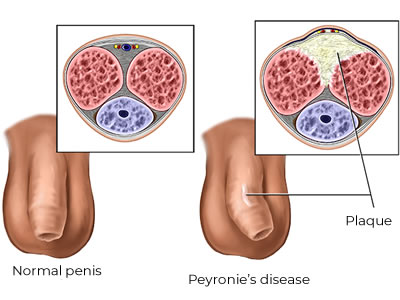
Peyronie's disease is a condition that causes the buildup of hard deposits in one of the penile sheats, which leads to painful erections, penile curvature and shortening of the penis.
- It is a relatively common disease
- It occurs at any age, but usually between the ages of 50 and 60
Peyronie's disease can be associated with high blood pressure, diabetes, blood fat disorders, as well as the formation of hard deposits on the tendons of the hand (Dupuytren's contracture).
What Are The Basic Characteristics Of Peyronie's Disease?
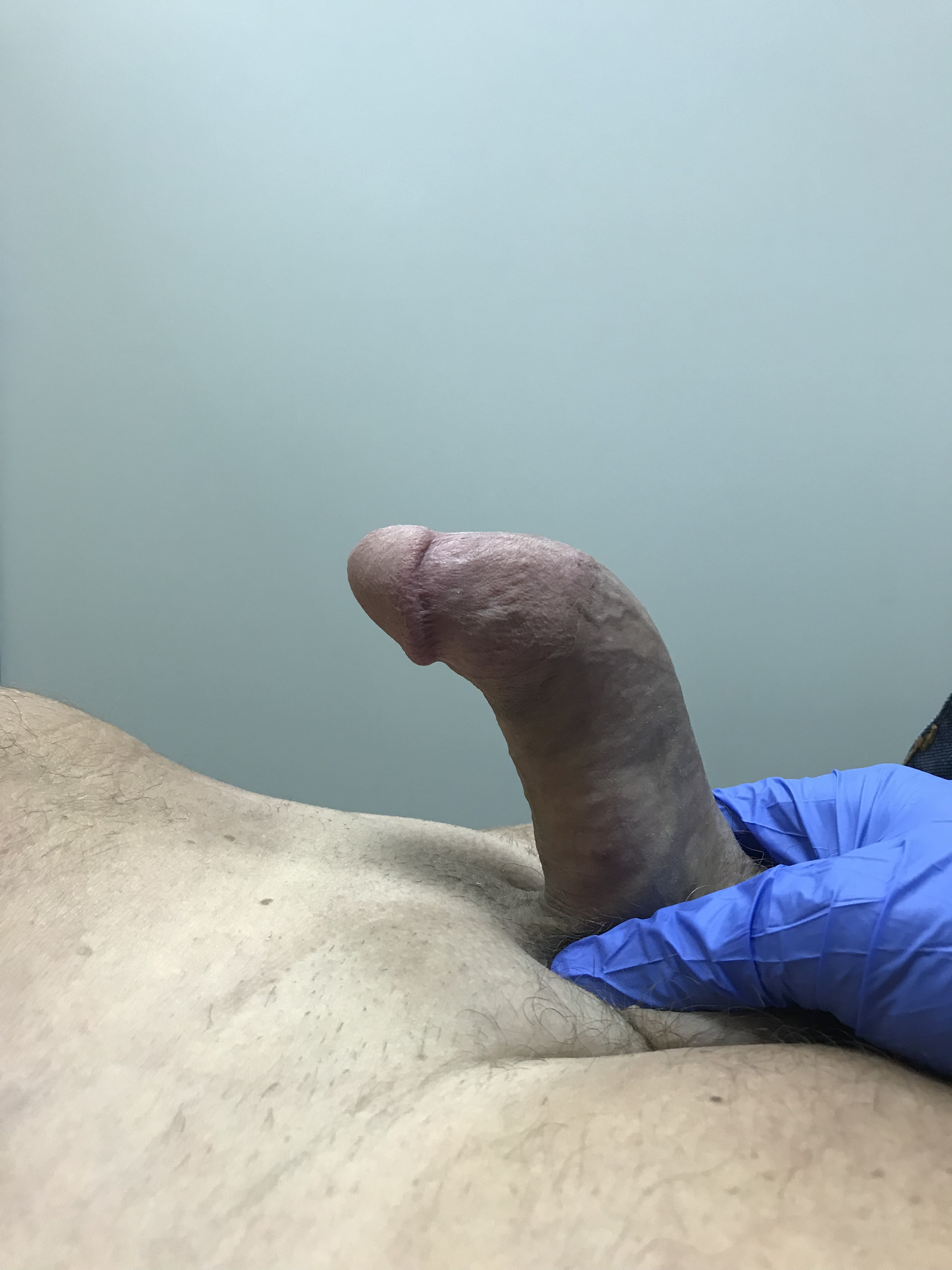
- Existence of hardening (plaque) on the body of the penis
- Curvature (deformity) of the penis
- Shortening of penile length
- Painful erections
- Sexual intercourse difficult or completely disabled
- Erectile Dysfunction (Impotence)
How is Peyronie’s disease diagnosed?
- Based on the above symptoms
- Clinical examination confirming the existence of hardening - plaque on the penis
- Ultrasound examination of the penis
- A photo of a penis in an erection
- Erection test - eliciting a medicated, artificial erection in an outpatient setting
Why causes Peyronie's disease?
To date, it has not been established what is the direct cause of this disease, but recurrent microtrauma, based on a congenital predisposition, is thought to lead to an inflammatory reaction, then to fibrin deposition, and subsequently to calcium deposition. All this is manifested in the form of hardening of the penis sheath we call plaque.
Phases of Peyronie's disease
- Active (disease progression phase) - characterized by painful erections and deformities that increase in size, lasting generally about 12 months.
- Stable (disease resting phase) - characterized by the absence of pain. The curve of the penis is constant at this stage and does not change any more.
How is Peyronie's disease treated?
Treatment for Peyronie's disease can be conservative and surgical.
- Non-surgical (conservative) treatment involves oral, topical and injection therapy.
- Oral therapy is NOT effective according to all published studies. During the active phase, some anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. ibuprofen) may be administered to reduce pain. Other oral therapies, which, unfortunately, are still frequently prescribed (e.g., vitamin E, Potaba, Colchicine, tamoxifen, pentoxifylline) are NOT effective and cannot resolve Peyronie's disease.
- Topical therapy may in some cases affect the maintenance and reduction of plaque (e.g. verapamil gel).
- Injectable (intralesional) therapy can sometimes produce good results, only when administering the substance - clostridial collagenase (Xiapex) into the plaque itself. Other substances (e.g. steroids) have no effect in the treatment of Peyronie's disease and are not recommended.
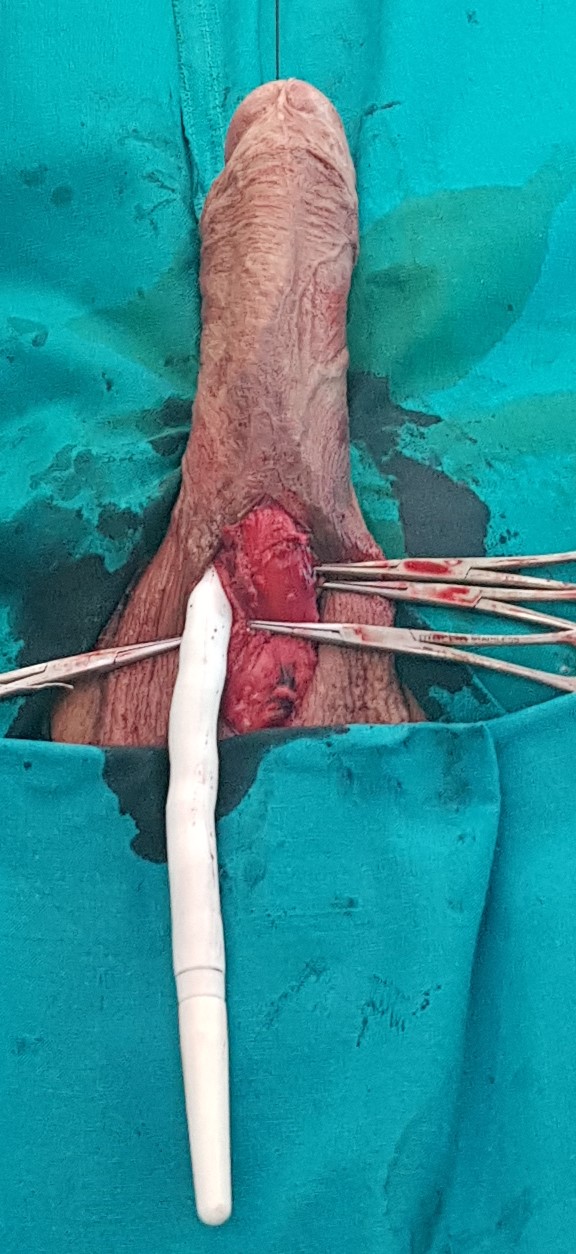
- Surgical (surgical) treatment of Peyronie's disease.
Intraoperative video AMS 700 demo prosthesis
The aim of surgical treatment is to correct the curvature of the penis with complete restoration of penile function.
One of the most important steps is the evaluation of the surgeon at what point in time to do the surgery.
Surgery may be performed under general or regional (spinal) anesthesia, when the patient may be awake during the operation.
There are three basic surgical approaches:- Deformation correction by penile plication
- Deformity correction using grafts (“patches”)
- Implantation of penile prosthesis
When deciding on the choice of surgical technique, the surgeon takes into account the patient's age, the existence of erectile dysfunction, plaque size, the degree of curvature of the penis, the length of the quiet phase, the quality of the tissue and vascularization.
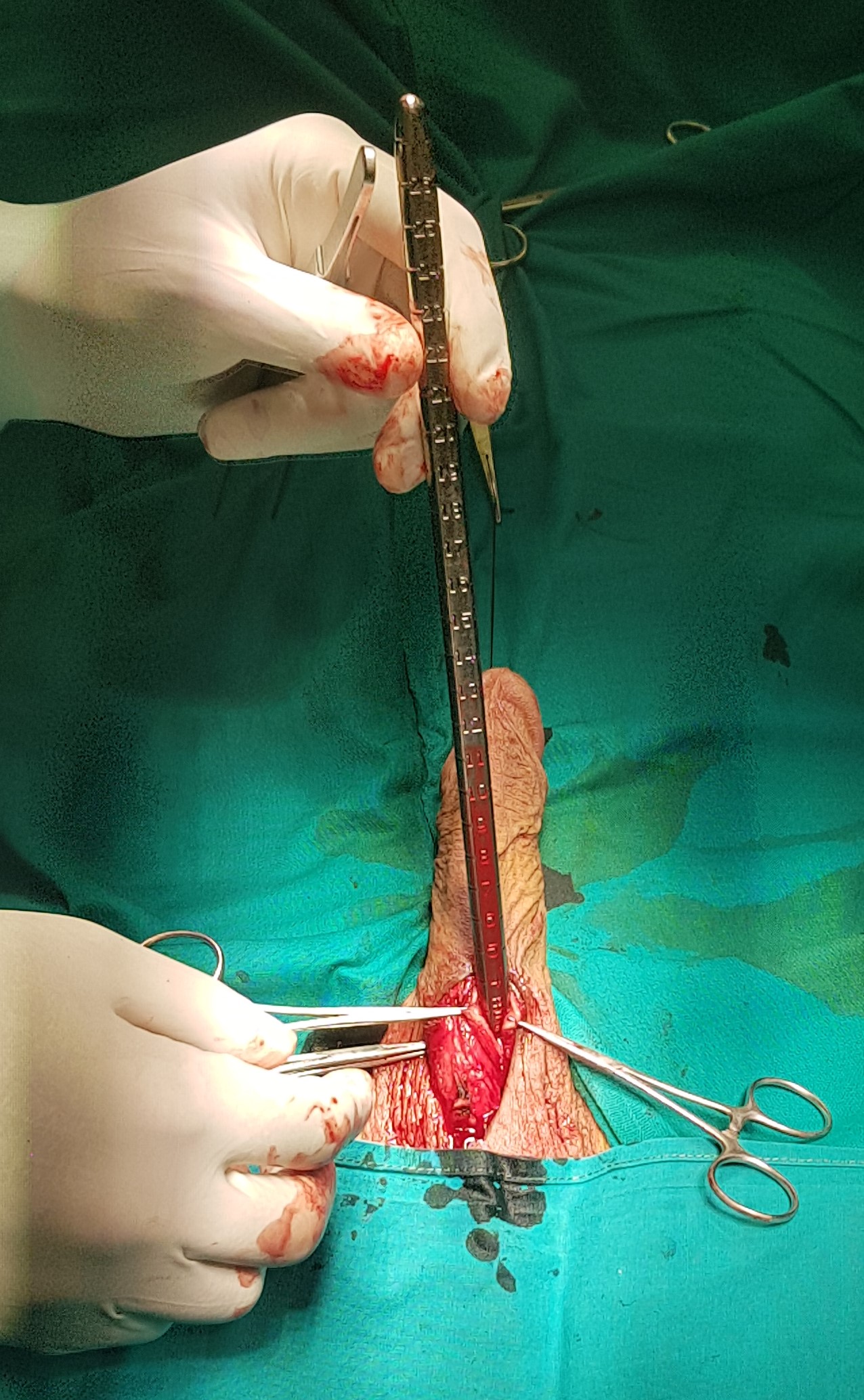
- Correction of the deformity with the plication of the penis involves shortening the longer side of the penis in order to correct the curvature. This method is less commonly used, and is only applicable if it is a minor deformation, i.e. if the curvature is less than 30 °.
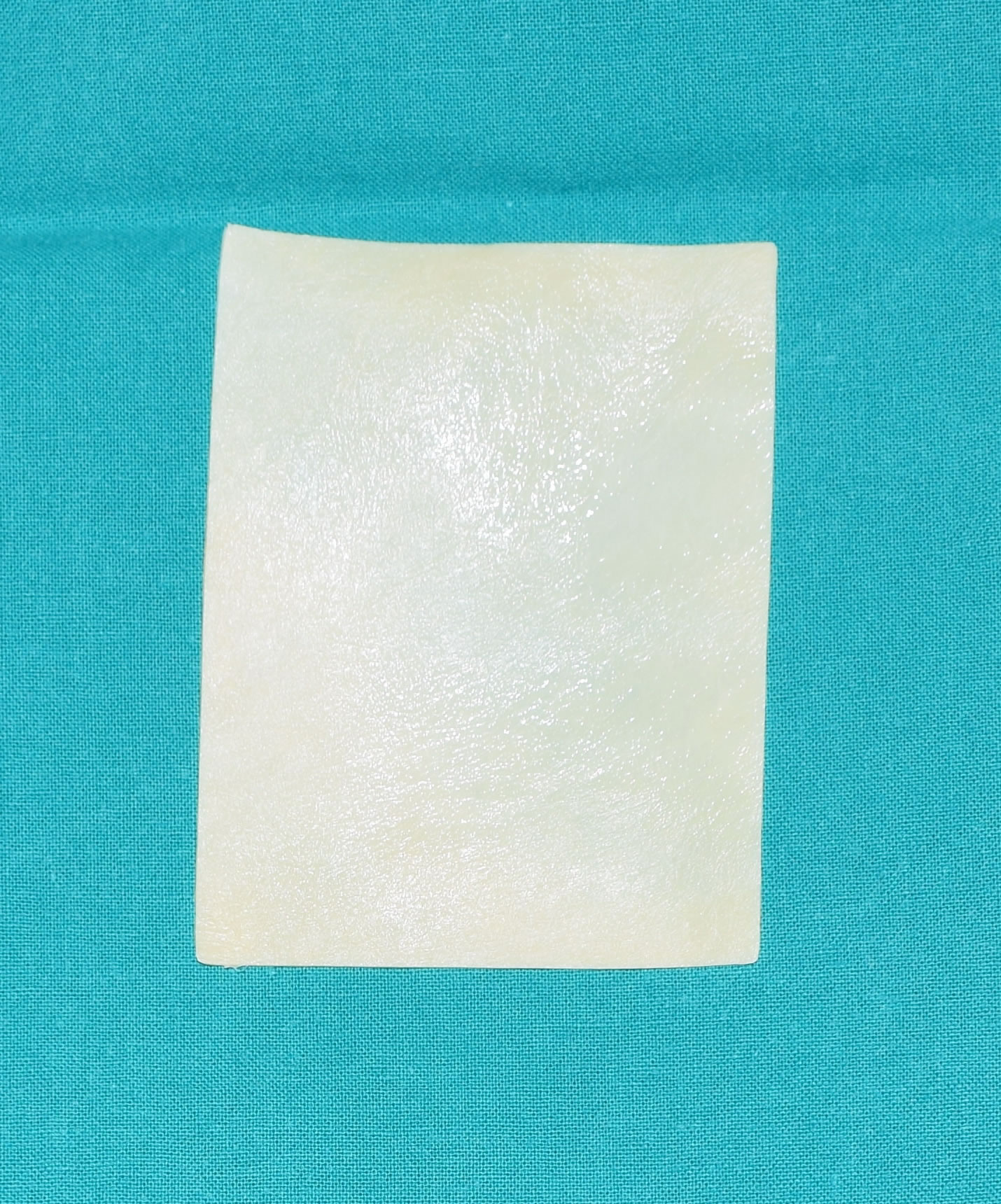
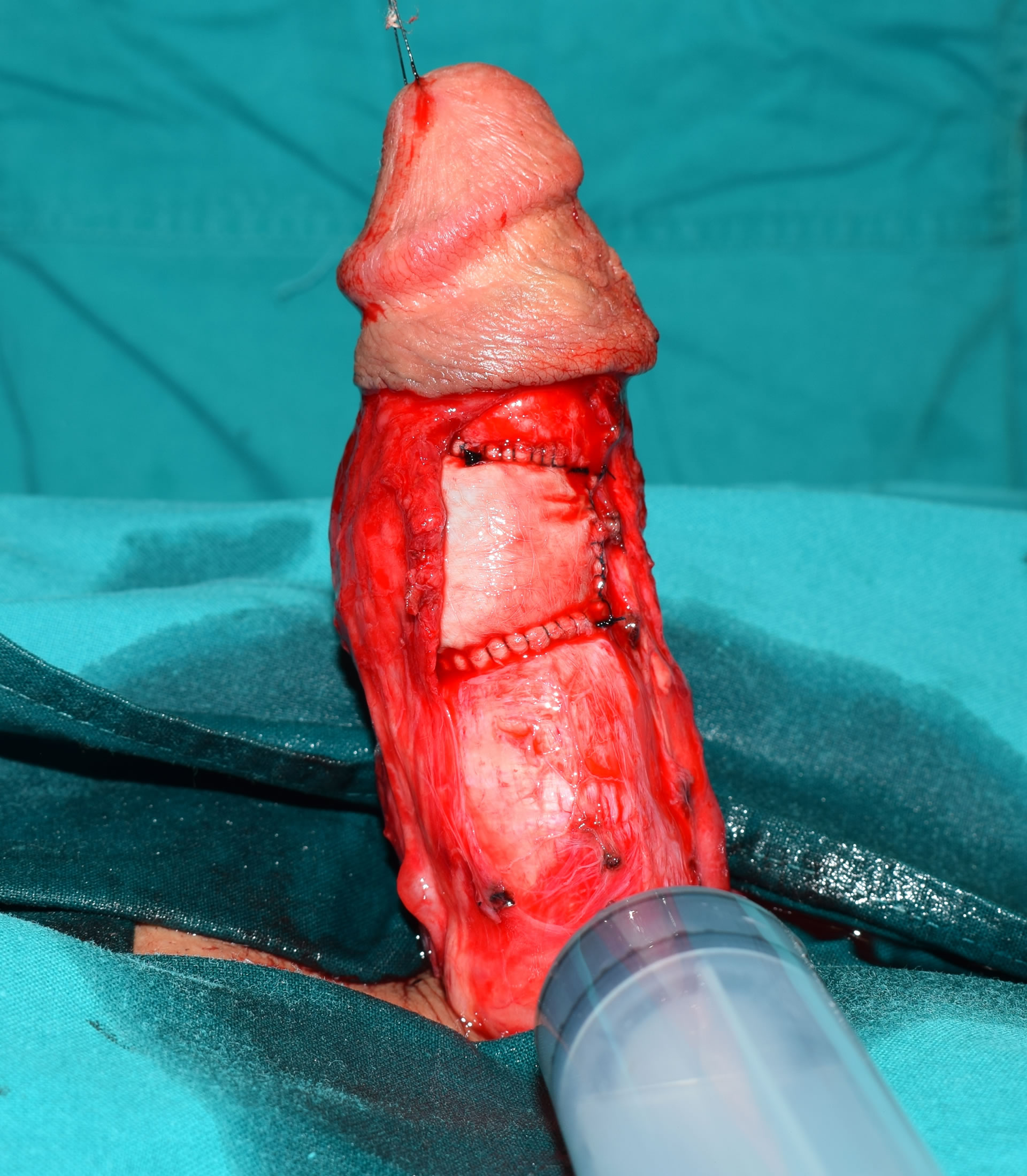
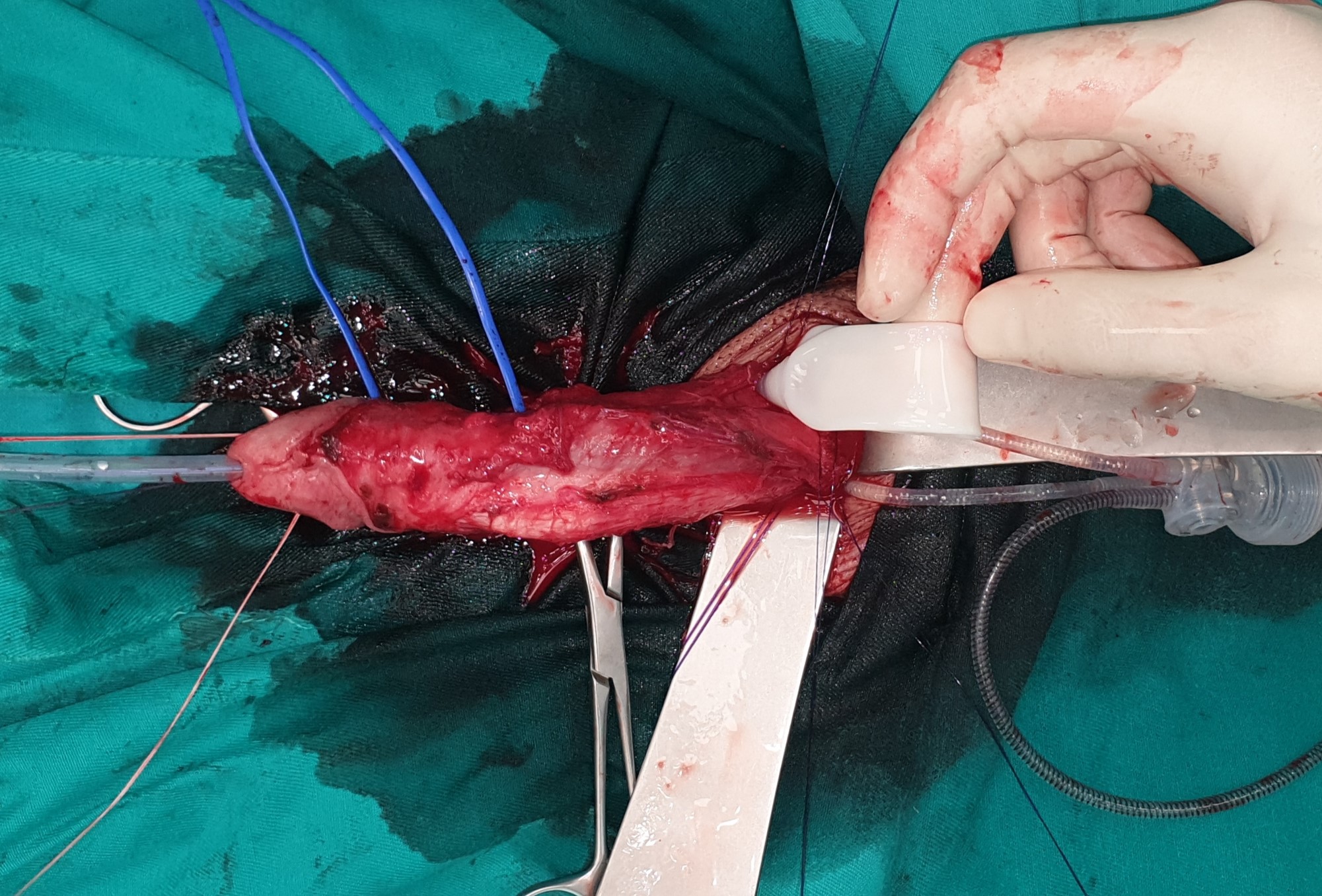
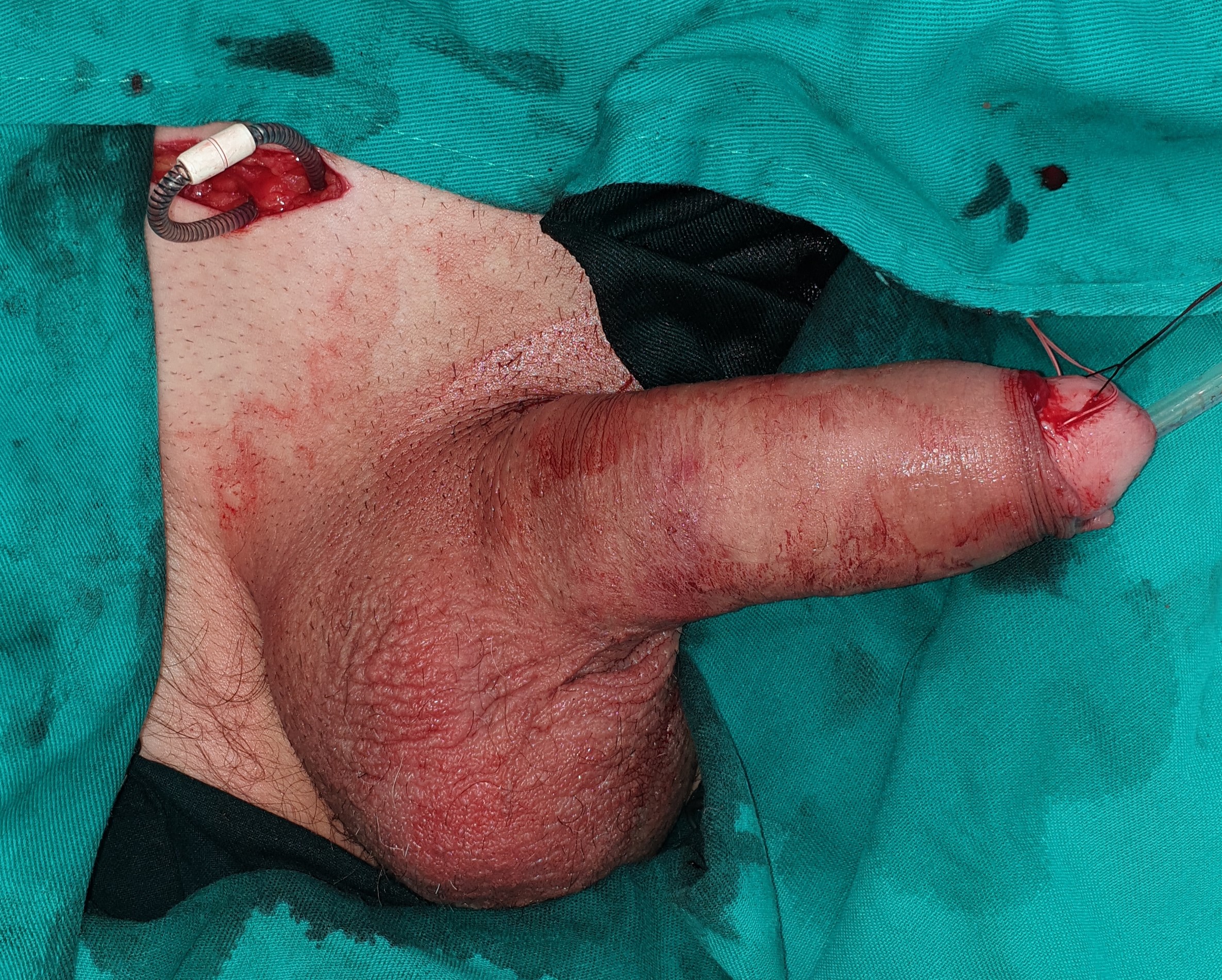
- Graft deformity correction aims at complete restoration of anatomy and function, with penile extension. The plaque itself intersects, the shortened side is thus corrected and extended, and the defect is reconstructed with a graft. During the operation, a geometric method is used to completely correct the deformity. The basic prerequisite for choosing this operating technique is the preserved erectile function.
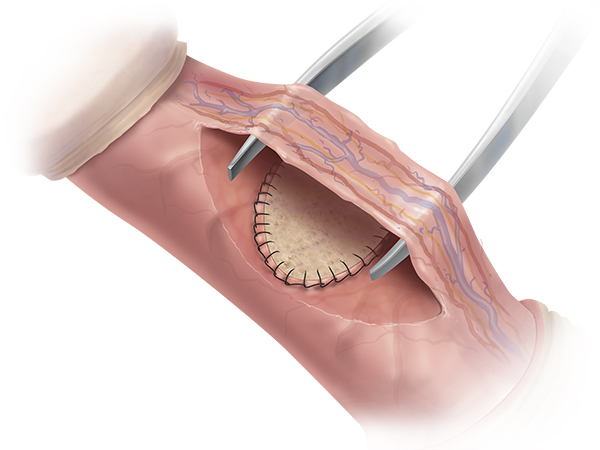 Graft deformity correction
Graft deformity correction 
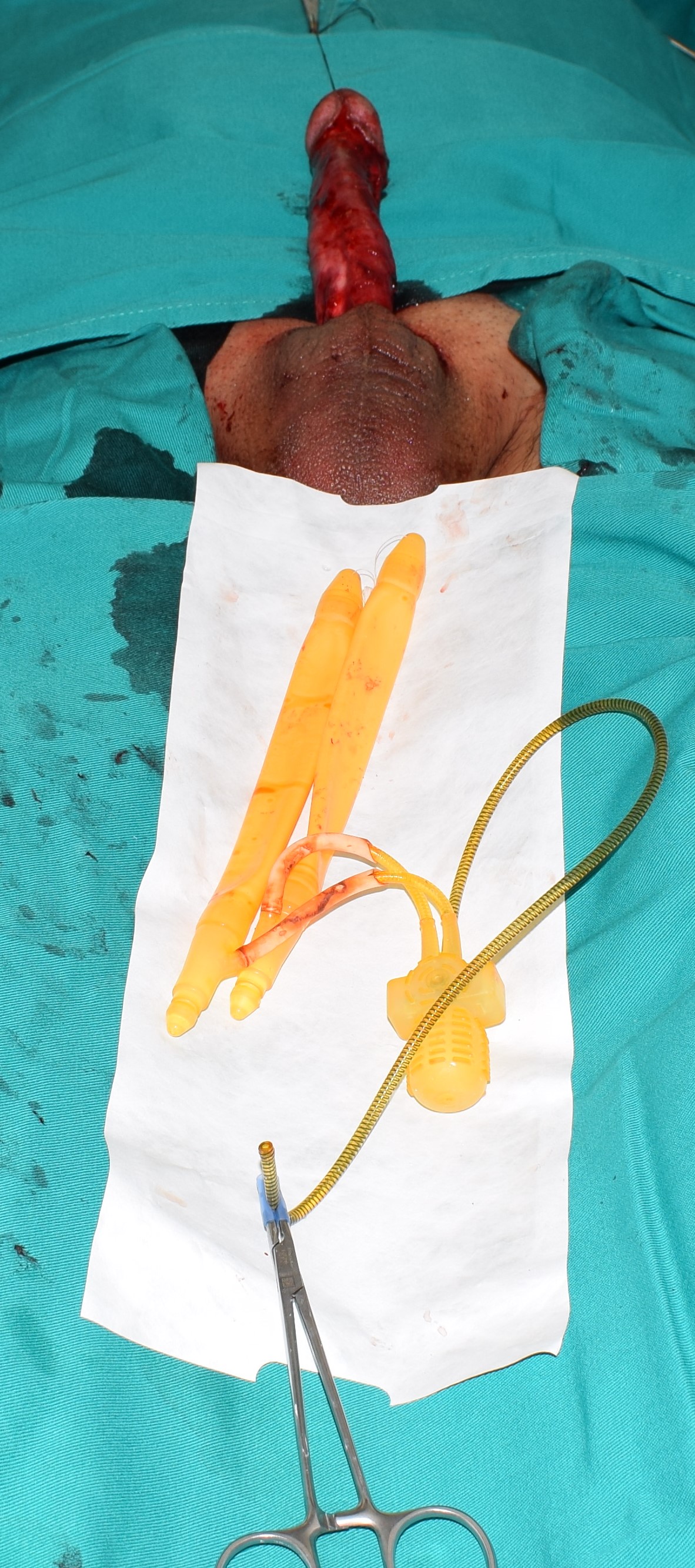
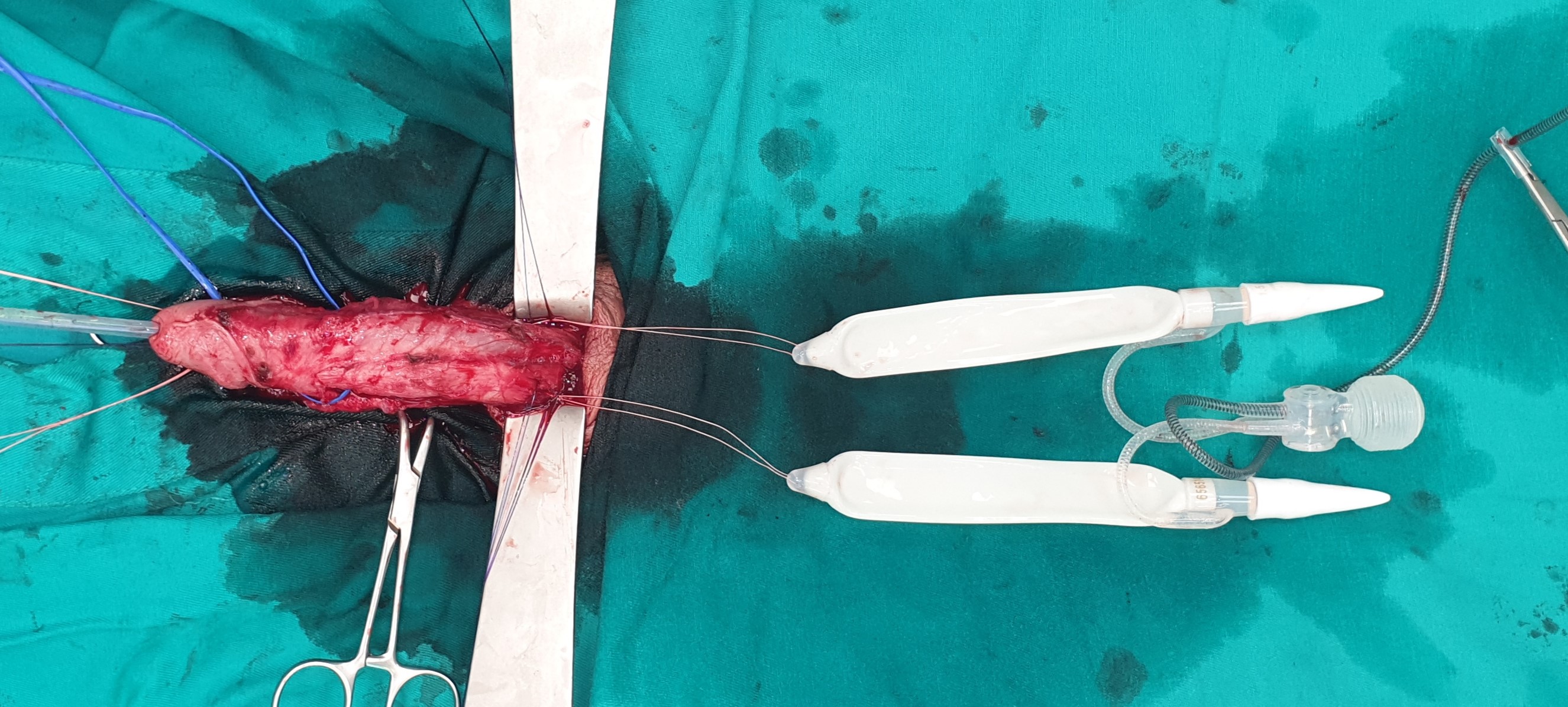
- The implantation of the penile prosthesis is performed if Peyronie's disease is accompanied by erectile dysfunction. Today, there are two basic types of penile prostheses: semi-rigid and inflatable. During surgery, deformity is corrected and a suitable implant is placed. The aim of the surgery is to restore the length of the penis, correct deformity and allow penetration. Thanks to the operating technique used, after the implantation, the penis has a completely normal appearance and it is not possible to visually detect any of the components of the penile prosthesis. Sexual intercourse with this type of prosthesis is the closest to the natural relationship and neither partner can feel the presence of penile prostheses during the relationship. You can read more about types of penile prostheses and their installation here
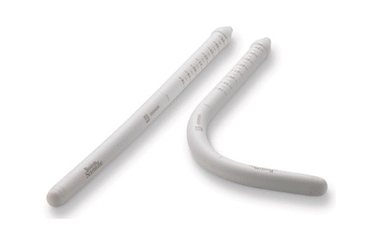

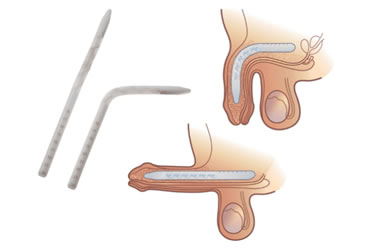
Semi-rigid prosthesis

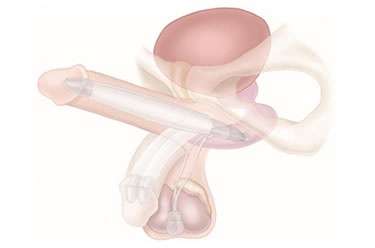
Inflatable prosthesis
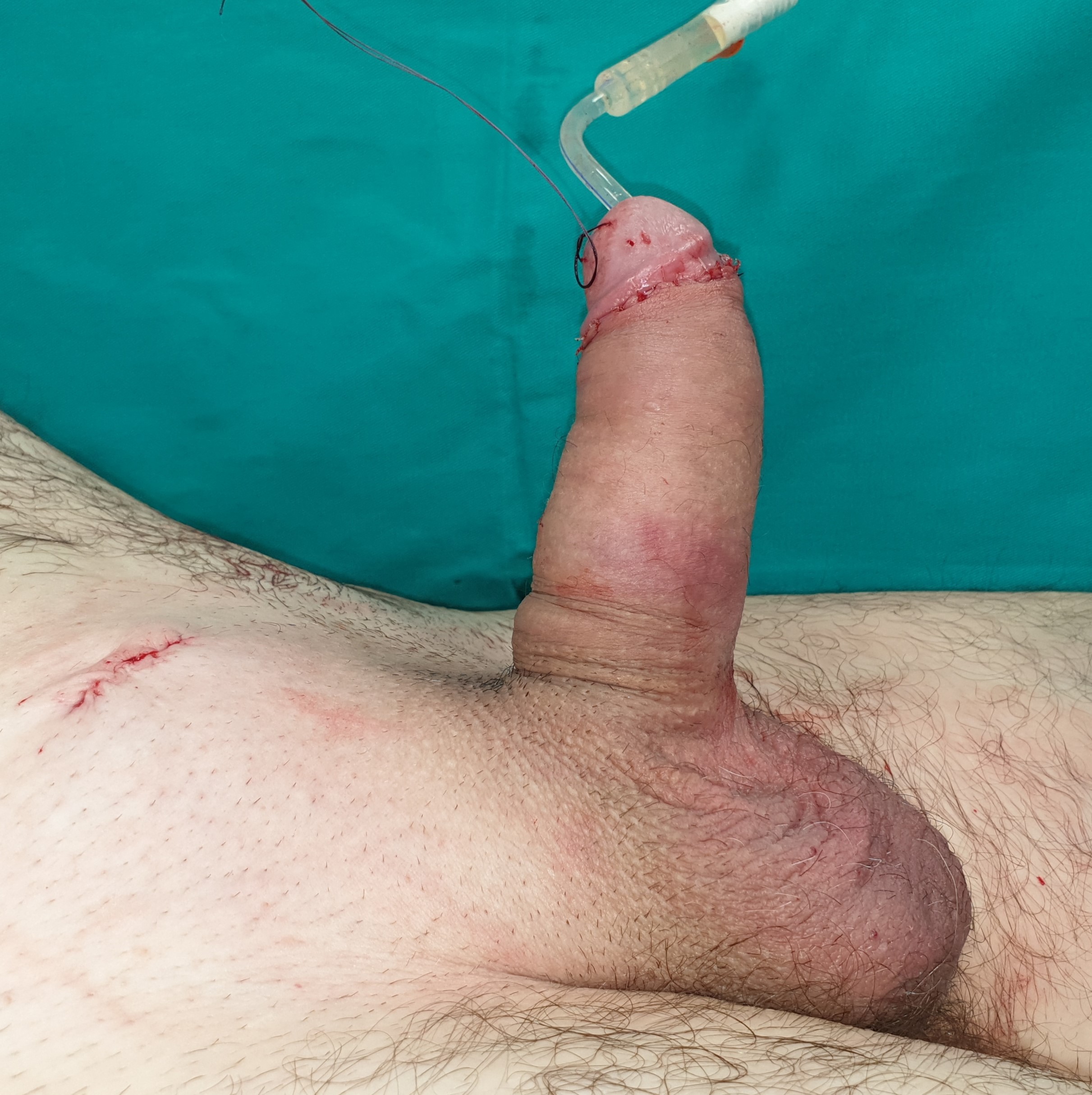
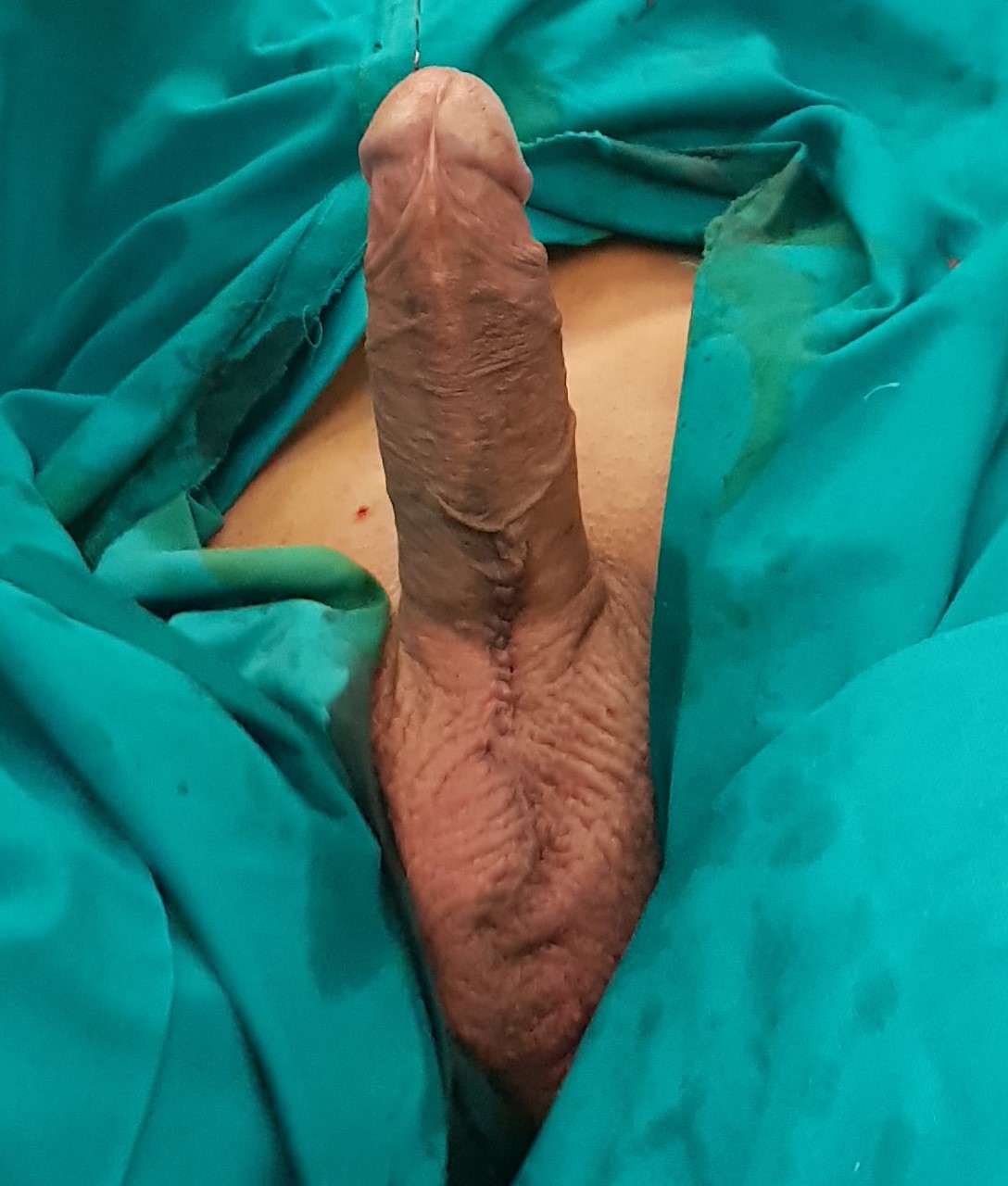
How does the postoperative recovery look like?
- After surgery, the patient stays in the hospital for a day or two.
- Antibiotic therapy and painkillers are prescribed.
- A compression bandage over the next 7 days is required.
- For wounds on the skin, resorptive stitches are generally used, which break down on their own, so they do not need to be removed.
- If surgery was performed using a graft, the patient is advised to use drugs to enhance the circulation in the penis, as well as to use traction devices or a VEP pump to maximize the effect of the surgery and prevent complications.
- If surgery is performed by implantation of the penile prosthesis, the patient is trained to use it.
- It is advised to abstain from sexual relations for 4-6 weeks.
The aim of surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease is to achieve the maximum functional and aesthetic result, which enables sexual relations and thus significantly contributes to the quality of life of the patient and the partner.